INDIANAPOLIS, IN (Oct 22, 2020) –Research by Jobvite finds gender differences at the application level are largely consistent with those at the employment level. Jobvite goes on to find that gender differences at the application level are, in-part, driven by differences in skills and certifications. “What is exciting about these findings are that in some instances we have an opportunity to nudge diversity and inclusion by including very similar, more broadly held skills in the job description,” said Jobvite Chief Data Scientist Morgan Llewellyn, PhD, that can then lead to more diversity of applicants.
Employment by gender is a well tracked labor force statistic. According to a 2018 release by the Bureau of Labor Statistics, women comprise almost 50% of employed workers.1 However, at an industry or position level the male to female employee ratios can swing wildly. For instance, women make up nearly 80% of teachers, whereas men comprise about 80% of software developers.
While insightful from a macro-economic perspective, employment is a lagging indicator as it considers those already employed. Leveraging deep learning algorithms, Jobvite is able to provide recruiters an early and complete picture of applicant pool diversity. What’s more, Jobvite compiles these statistics using non-personally identifiable information (PII) or self-reported information. This allows Jobvite to provide an earlier, more complete picture of diversity within talent pipelines over standard self-reporting metrics.
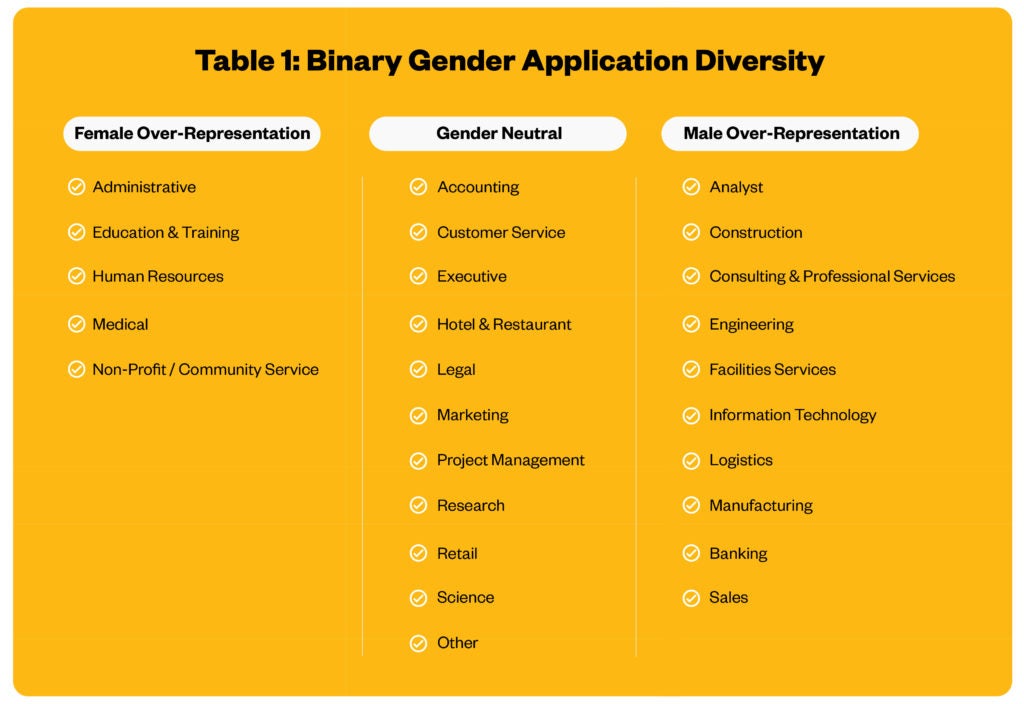
Table 1 presents results on the estimated percentage of male and female applicants for selection of positions. In this table, “Over-Representation” indicates positions where more than 60% of applicants come from a single gender, whereas “Gender Neutral” indicates an approximate 50-50 split in applicant gender.
Evaluating Table 1 is largely confirmatory with at least one unexpected insight. As expected for medical positions, such as nursing, applicants tend to be women whereas applications tend to come from men for IT roles. Encouraging to D&I initiatives seeking greater female representation in the boardroom is that women comprised at least 40% of executive applications during the first half of 2020 on the Jobvite platform.
To understand, in-part, why gender gaps exist at the application level, it is insightful to examine gender gaps in skills and experience. For example, over 60% of resumes that contain the programming language SQL and 70% of resumes that contain Java programming are male. However, nearly 80% of resumes that contain a registered nurse certification or ADP skills are female. Results like these support the conclusion that gaps in applicant diversity can be attributed, in part, to underlying skills gaps.
What tangible steps can recruiters take to increase the diversity of their applicant pool? Recruiters can promote inclusion and diversity efforts through awareness of how requested skills and experiences impact the diversity of the applicant pool. While perhaps more effective for some roles than others, there are opportunities to broaden applicant pools and diversify job appeal by requesting more widely held skills and eschewing non-essential experience.
For example, in the tech space substituting a SQL database administration skill for MySQL database administration doubles the ratio of women possessing the skill. Equally important is understanding the impact of how “nice to haves” can impact D&I. “Experience managing AR/AP a plus” may inadvertently bias the applicant pool as men tend to have this specific experience at higher rates; despite women being more likely to work in AR/AP.
“Our findings suggest recruiters may encourage a larger, more diverse applicant pool through awareness over their selection of skills and experiences,” Llewellyn said. “I can think of no better application of AI than seeking to inform diversity and inclusion. We look forward to supporting the diversity and inclusion conversation through our on-going work on identifying similar, more inclusive, skills.”
About These Results
Applicant data is taken from Jobvite positions posted in 2020. Jobvite uses advanced natural language processing to properly identify and categorize job descriptions. Jobvite uses deep learning over a candidate’s non-PII information to obtain an estimate of the candidate’s binary gender and race. To learn more about this and other Jobvite AI initiatives, visit Jobvite.
About Jobvite
Jobvite is leading the next wave of talent acquisition innovation with a candidate-centric recruiting model that helps companies engage candidates with meaningful experiences at the right time, in the right way, from first look to first day. The Jobvite Talent Acquisition Suite weaves together automation and intelligence in order to increase recruiting speed, quality, and cost-effectiveness. Jobvite is proud to serve thousands of customers across a wide range of industries including Ingram Micro, Schneider Electric, Premise Health, Zappos.com, and Blizzard Entertainment. To learn more, visit www.jobvite.com or follow the company on social media @Jobvite.
1https://time.com/5766787/women-workforce/