The talent environment remains highly competitive amidst an uncertain economic climate. And it requires companies to focus on increasing efficiencies to achieve their hiring goals.
To enhance the speed of recruitment processes, some businesses have pursued automating their hiring workflows. While recruiting automation has empowered companies of all sizes for more than two decades to streamline hiring tasks, increase recruiter productivity, speed time-to-hire, and reduce cost-per-hire, AI is newer to talent acquisition, and it has the attention of talent teams.
Defining and Distinguishing Between Recruitment Automation and AI
Automation and AI are not synonymous in hiring. These two concepts are often used interchangeably, but they are distinct with their own ethical and technological implications.
Recruiting automation streamlines the recruiting process, taking tedious tasks away from hiring professionals, and freeing them up to do more important tasks like nurturing relationships, promoting the company’s employer brand, and developing more strategic recruiting strategies, including diversity, equity, inclusion, and belonging (DEIB).
While automation is one of the precursors to the development of AI technologies, automation lacks the learning and decision-making capabilities of AI.
Artificial intelligence enables software to augment decision making processes, encompassing areas such as machine learning, natural language processing, and pattern detective. AI has the power to learn and evolve, responding to data inputs and building upon that knowledge to continually improve its ability to perform tasks.
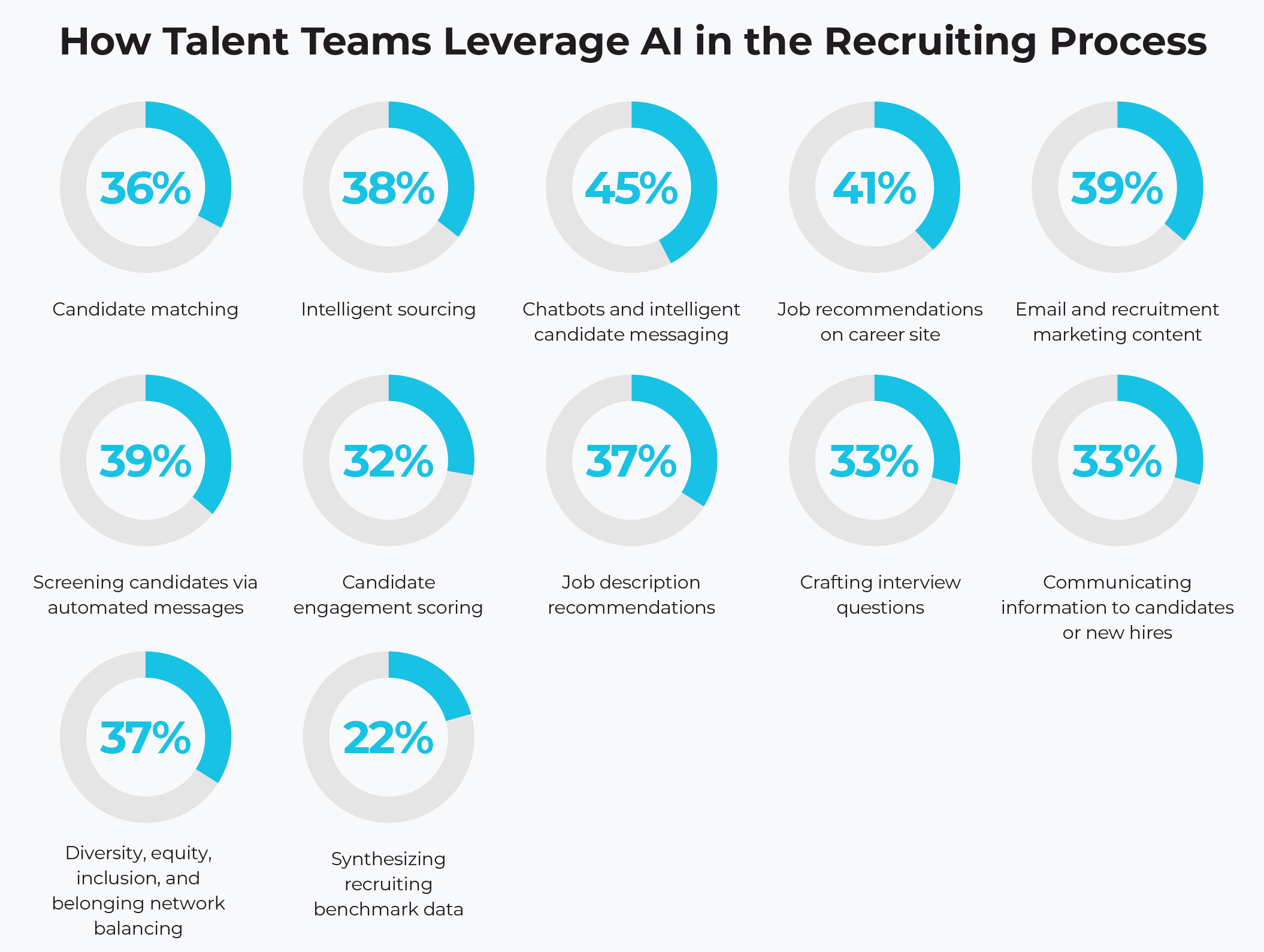
Leveraging AI in recruitment allows for greater efficiency and effectiveness, ultimately leading to better talent acquisition outcomes. For example, AI can assist in screening resumes, identifying the most qualified candidates, and even providing insights into potential fit of candidates.

Examining the Use of AI in Hiring
Where recruiters have previously leaned on applicant tracking systems and recruitment automation, enterprises are now incorporating more advanced solutions for their hiring efforts.
It’s important to note that AI is not as new to recruiting as some companies may believe. Since February 2023, the introduction of Generative AI has dominated news headlines and impacted the accessibility of artificial intelligence for individuals and hiring teams alike.
However, it is important to note that free tools take proprietary data, so companies no longer have control over protecting personal identifiable information (PII). To remedy this, it is important to be aware of the risks and consider steps to mitigate data privacy issues.
Relying on more established AI-powered tools is a solid strategy for those organizations looking to make their hiring processes more intelligent. By allowing AI to inform decision making, recruiters can focus on activities where they provide the most value, such as selling the role, negotiations, community building, and personalization.
Challenges with AI: Skepticism in Recruiting
For all the promise of AI-powered technologies, some talent acquisition and recruiting practitioners are risk-averse when it comes to adopting these newer technologies.
- Bias in Hiring: One of the greatest concerns of using AI in recruiting is the introduction of bias in the selection process. Without appropriate safeguards in place, AI can reflect the negative patterns it encounters. Because existing data sets inform AI tools on what to look for when defining qualified candidates, there have been very public instances where AI reinforces prevailing gender, racial, wealth or other biases.
- Recent AI Legislation: To combat the challenges of AI, new laws are being written to protect against it. According to the National Conference of State Legislatures, in 2023, 18 states and Puerto Rico adopted or enacted artificial intelligence bills of varying degrees to evaluate, study, limit or regulate how AI is used.
- Data and Privacy: Protecting sensitive candidate and hiring data is crucial to maintaining operations and ensuring compliance for employers today. Companies must keep the data as secure as possible and process as little personal identifiable information as possible.
- Concerns about Obsolescence: Talent teams that embrace automation, analysis, and insights that AI provides will likely have greater job security and a more strategic role within their organization. AI-powered recruiters have more opportunities to grow and achieve impactful recruiting outcomes.
Final Thoughts: Striking the Right Balance of AI and Human Ability
While efficiency gains have been realized through AI-powered tools, many recruiting processes will benefit from further advances in AI. The challenge, however, is one that goes beyond technology.
The human element of recruitment remains crucial, and effective collaboration between HR professionals and AI-powered tools can significantly enhance the effectiveness of recruitment strategies. It requires people — TA experts, hiring managers, and recruiting professionals — to embrace both the risks and rewards of AI-powered solutions.
When it comes to adoption, remember, it is important to consider AI as a co-pilot or support mechanism. AI assistants should complement the work of recruiters. AI can elevate and empower human interactions, big picture thinking, creativity, and decision-making. However, AI will not, and should not, replace human judgment and experience. But there is a need to tread cautiously.
Organizations must invest in the right set of AI tools with a trusted provider that fits their culture, values, and hiring needs. Ultimately, as companies continue to navigate through the rapid changes presented by AI, the human element of hiring will continue to play a central role in how and where these technologies are adopted across the hiring lifecycle.





